반응형
There are several types of level transmitters, each based on different principles of operation for measuring the level of liquids or solids in tanks or vessels. Here's an overview of the most common types, their principles, and a description of their appearance.

1. Ultrasonic Level Transmitters
- Principle: These transmitters use ultrasonic sound waves. The device sends sound waves toward the liquid surface, and the time it takes for the waves to bounce back is measured. This time is used to calculate the liquid level.
- Common Applications: Ideal for measuring the level of liquids and slurries in open and closed tanks.
- Appearance: Typically, it has a cylindrical sensor or a small cone-shaped device placed at the top of the tank.

2. Radar (Microwave) Level Transmitters
- Principle: Radar transmitters emit microwave radar signals that reflect off the surface of the liquid. The time it takes for the signal to return is used to calculate the liquid level.
- Common Applications: Used for measuring the level of corrosive liquids, slurries, and even solids in harsh environments.
- Appearance: It usually has a dome-shaped or horn antenna mounted at the top of the tank.

3. Capacitive Level Transmitters
- Principle: These transmitters use changes in capacitance between two electrodes. The change in the liquid level causes a variation in the dielectric constant, which is measured and converted into a level reading.
- Common Applications: Used for conductive and non-conductive liquids as well as granular materials.
- Appearance: Usually consists of a probe or rod that extends vertically into the tank.

4. Hydrostatic Pressure Level Transmitters
- Principle: Measures the pressure exerted by the liquid column at the bottom of the tank. The pressure increases with the height of the liquid, and this is converted into a level measurement.
- Common Applications: Suitable for liquids in open or closed tanks.
- Appearance: A small sensor is installed at the bottom of the tank or inside the vessel.

5. Magnetostrictive Level Transmitters
- Principle: A magnetic float moves along a probe, and its position is detected by a magnetic field. This position is then converted into a level measurement.
- Common Applications: Used for measuring the level of clean liquids in tanks.
- Appearance: A long probe with a float attached to it, inserted into the tank.

6. Displacer Level Transmitters
- Principle: Based on Archimedes' principle, this transmitter uses a displacer suspended in the liquid. As the liquid level rises, the displacer experiences a buoyant force that changes its weight. This change is used to determine the level.
- Common Applications: Used for measuring liquids and interfaces between liquids of different densities.
- Appearance: A cylindrical displacer hung inside the tank, connected to a sensor.

7. Guided Wave Radar (GWR) Level Transmitters
- Principle: These transmitters send microwave pulses down a probe or rod. The pulses reflect off the surface of the liquid, and the time of flight is used to calculate the level.
- Common Applications: Ideal for liquids, slurries, and even powders.
- Appearance: A rod or cable probe that extends into the tank, with electronics mounted on the top.
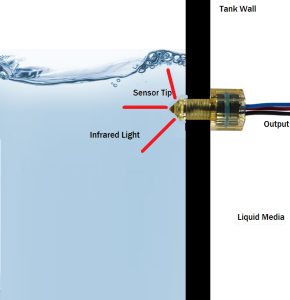
8. Optical Level Transmitters
- Principle: Uses light to detect the liquid level. The sensor emits a beam of light, and the reflection is used to determine if the liquid is present at a certain level.
- Common Applications: Suitable for smaller tanks with clean, transparent liquids.
- Appearance: A small, compact sensor typically placed at a specific level inside the tank.

9. Vibrating (Tuning Fork) Level Transmitters
- Principle: Consists of a tuning fork that vibrates at a certain frequency. When the fork is submerged in liquid, the vibration frequency changes, which is detected and used to determine the level.
- Common Applications: Suitable for detecting the presence of liquids and solids.
- Appearance: A tuning fork-shaped sensor that extends into the tank.
If you would like, I can generate a visual representation or image of any of these transmitters.
반응형
'엔지니어링 > Level' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 레벨 스위치 - 진동 포크형(Vibration Fork Type) (0) | 2022.11.08 |
|---|---|
| 차압(Differential Pressure) 레벨 계측기 적용 요건 (0) | 2022.10.20 |
| 자기변형식(Magnetostrictive) 레벨 계측기 적용 요건 (0) | 2022.10.20 |
| GWR(Guided Wave Radar) 레벨 계측기 적용 요건 (0) | 2022.10.20 |
| 레벨 게이지(Level Gauge) 적용 요건 (0) | 2022.10.20 |




댓글